Passive Solar Tracking
Having the maximum amount of absorber area directly facing the sun causes superior solar collector performance. Because of their round design, Solar Panels Plus evacuated tube collectors are able to passively track the sun, meaning that they are always pointed directly at the sun and can absorb solar thermal energy evenly all day long.
This is important, particularly if the heat is needed throughout the day without using a large thermal storage system. Evacuated tube solar collectors are great for everything from making plain old hot water, to solar heating, solar air conditioning, commercial water heating or manufacturing process heat.
By tracking the sun from early morning until late afternoon, more heat is generated by the collector which means that your existing energy source will be used less, saving money and helping conserve precious non-renewable resources
Flat-plate collectors, on the other hand, only directly face the sun during midday which decreases their maximum daily heat output, lowers the heat available during morning and afternoon, and, causes the need for larger storage in many applications.
It’s no wonder that evacuated tubes are quickly becoming the solar collector of choice for commercial and residential users throughout the world.
Passive Solar Tracking
Having the maximum amount of absorber area directly facing the sun causes superior solar collector performance. Because of their round design, Solar Panels Plus evacuated tube collectors are able to passively track the sun, meaning that they are always pointed directly at the sun and can absorb solar thermal energy evenly all day long.
This is important, particularly if the heat is needed throughout the day without using a large thermal storage system. Evacuated tube solar collectors are great for everything from making plain old hot water, to solar heating, solar air conditioning, commercial water heating or manufacturing process heat.
By tracking the sun from early morning until late afternoon, more heat is generated by the collector which means that your existing energy source will be used less, saving money and helping conserve precious non-renewable resources
Flat-plate collectors, on the other hand, only directly face the sun during midday which decreases their maximum daily heat output, lowers the heat available during morning and afternoon, and, causes the need for larger storage in many applications.
It’s no wonder that evacuated tubes are quickly becoming the solar collector of choice for commercial and residential users throughout the world.
Incidence Angle Modifier (IAM)
IAM is the variance in output performance of a solar collector as the angle of the sun changes in relation to the surface of the collector.Solar Panels Plus evacuated tubes provide an important and measurable increase in efficiency in the morning and afternoon when the sun’s angle is between 40 and 80 degrees from perpendicular. The result is constant heat output for the better part of the day.
When solar energy is absorbed by a collector at an angle other than perpendicular, the performance of that collector changes and measuring the IAM provides an angle based performance factor. When the collector is perpendicular to the sun, a maximum value of 1 is achieved as the collector is receiving the maximum amount of radiation possible.
In the instance of flat-plate collectors, the maximum value of 1 is achieved at midday and is quite less during the morning and afternoon. The chart at the bottom of the page clearly shows this.
Our evacuated tube solar collectors, on the other hand, often provide performance values in excess of 1 during the morning and afternoon based on their cylindrical design, which allows the panels to reflect onto each other which can boost performance.
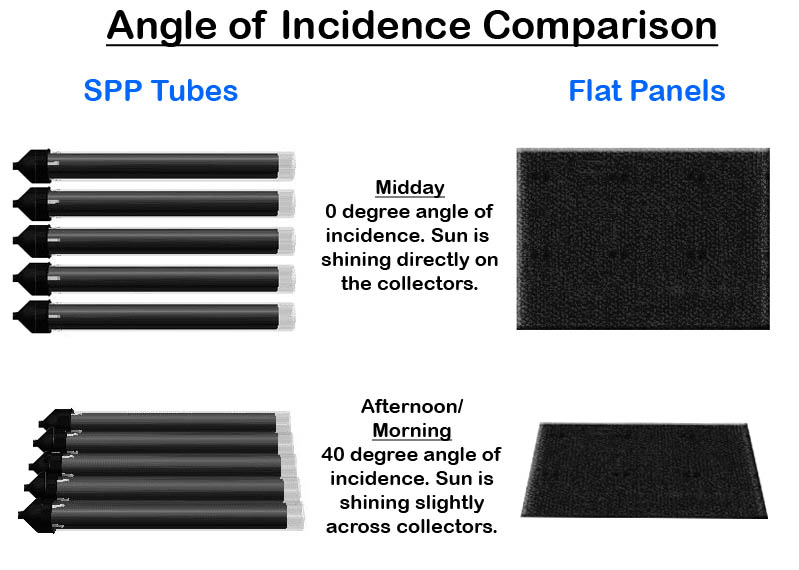
The diagram to the left further demonstrates the passive tracking of the sun by Solar Panels Plus evacuated tubes.
In the first picture (0 deg), the sun is directly perpendicular to the collector and is allowing the collector to absorb the maximum amount of sunlight available. The gaps in between the tubes do let some sunlight pass through but the collector still produces an IAM of 1.
In the next picture (40 deg), the sun is approximately 2 hours and 40 minutes before/after midday. The are no gaps in between the tubes and the sun is still perpendicular to the collector, allowing for the maximum amount of sunlight to be absorbed and reflected onto neighboring tubes, producing an IAM values of greater than 1 (peak performance).
As the angle of the sun increases beyond 40 deg the evacuated tubes begin to overlap and are exposed to less solar radiation. The surface area of the collector is still absorbing sunlight but performance is reduced due to the overlapping of the tubes. This has minimal effect on the overall daily performance of the collector because only a small percentage of sunlight falls beyond the optimal angle of 40 degrees (very early morning/very late afternoon)
The result of the IAM effect equates to approximately a 25% increase in heat output performance compared to flat-plate collectors with the same absorber area and under the same operating conditions. The IAM is extremely important to consider when comparing heat output of different solar collectors – especially when comparing flat-plate collectors to evacuated tube collectors.

The diagram to the left further demonstrates the passive tracking of the sun by Solar Panels Plus evacuated tubes.
In the first picture (0 deg), the sun is directly perpendicular to the collector and is allowing the collector to absorb the maximum amount of sunlight available. The gaps in between the tubes do let some sunlight pass through but the collector still produces an IAM of 1.
In the next picture (40 deg), the sun is approximately 2 hours and 40 minutes before/after midday. The are no gaps in between the tubes and the sun is still perpendicular to the collector, allowing for the maximum amount of sunlight to be absorbed and reflected onto neighboring tubes, producing an IAM values of greater than 1 (peak performance).
As the angle of the sun increases beyond 40 deg the evacuated tubes begin to overlap and are exposed to less solar radiation. The surface area of the collector is still absorbing sunlight but performance is reduced due to the overlapping of the tubes. This has minimal effect on the overall daily performance of the collector because only a small percentage of sunlight falls beyond the optimal angle of 40 degrees (very early morning/very late afternoon)
The result of the IAM effect equates to approximately a 25% increase in heat output performance compared to flat-plate collectors with the same absorber area and under the same operating conditions. The IAM is extremely important to consider when comparing heat output of different solar collectors – especially when comparing flat-plate collectors to evacuated tube collectors.


